46. Permutations
문제 설명
중복이 없는 정수 배열 nums가 주어질 때, 가능한 순열을 모두 반환하세요. 정답에 정렬은 필요하지 않습니다.
해결 방법
dfs(재귀)를 활용하여 순열을 구현한다.
결과부터 말하자면, 현재 만들고 있는 순열이 nums와 크기가 같아질 때, answer에 만든 순열을 넣는다. 프로세스는 아래와 같다.
- 시작 지점을 알리는
depth와 기존 배열을 복사해dfs에 넘긴다. - dfs의 종료조건은
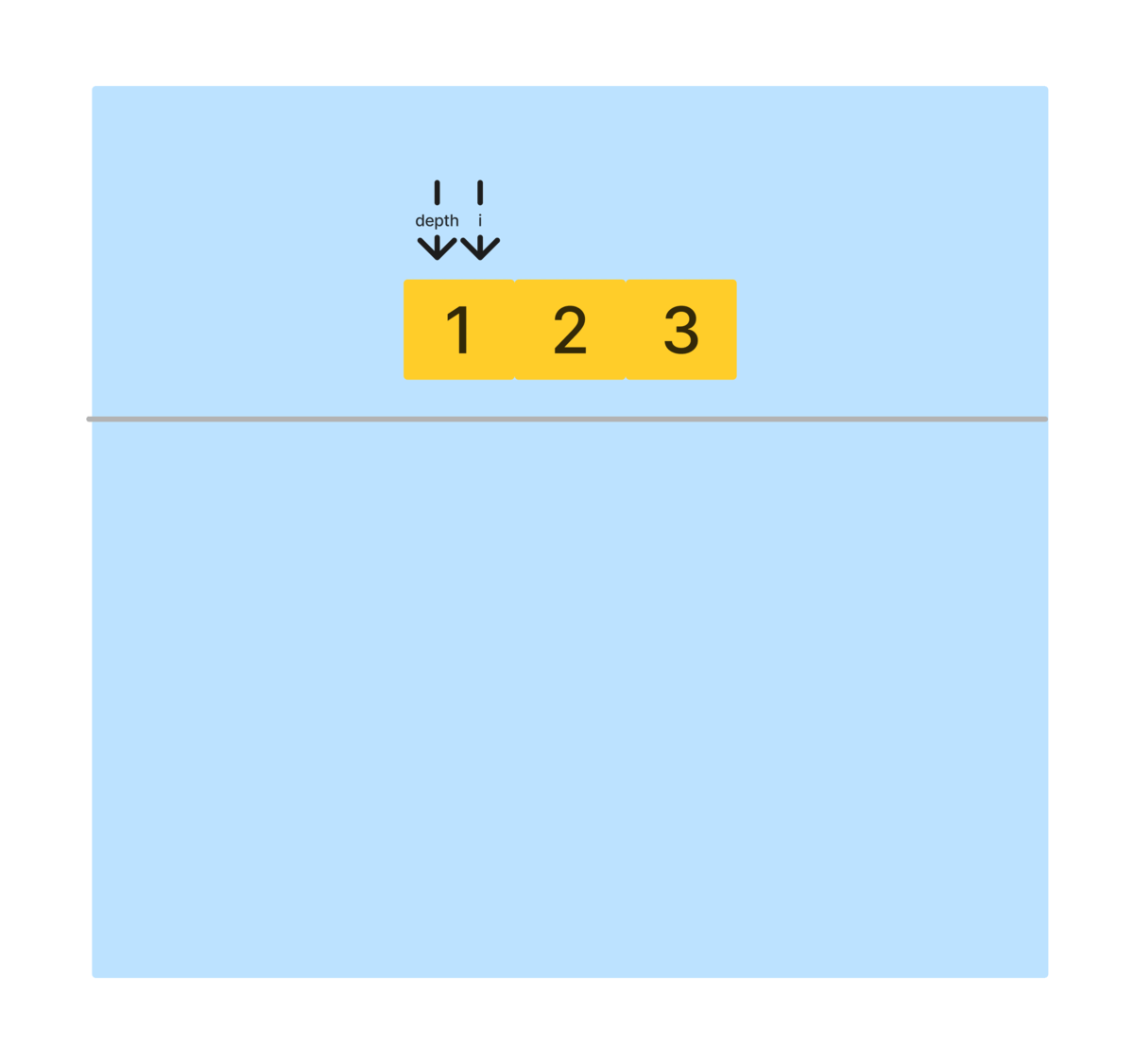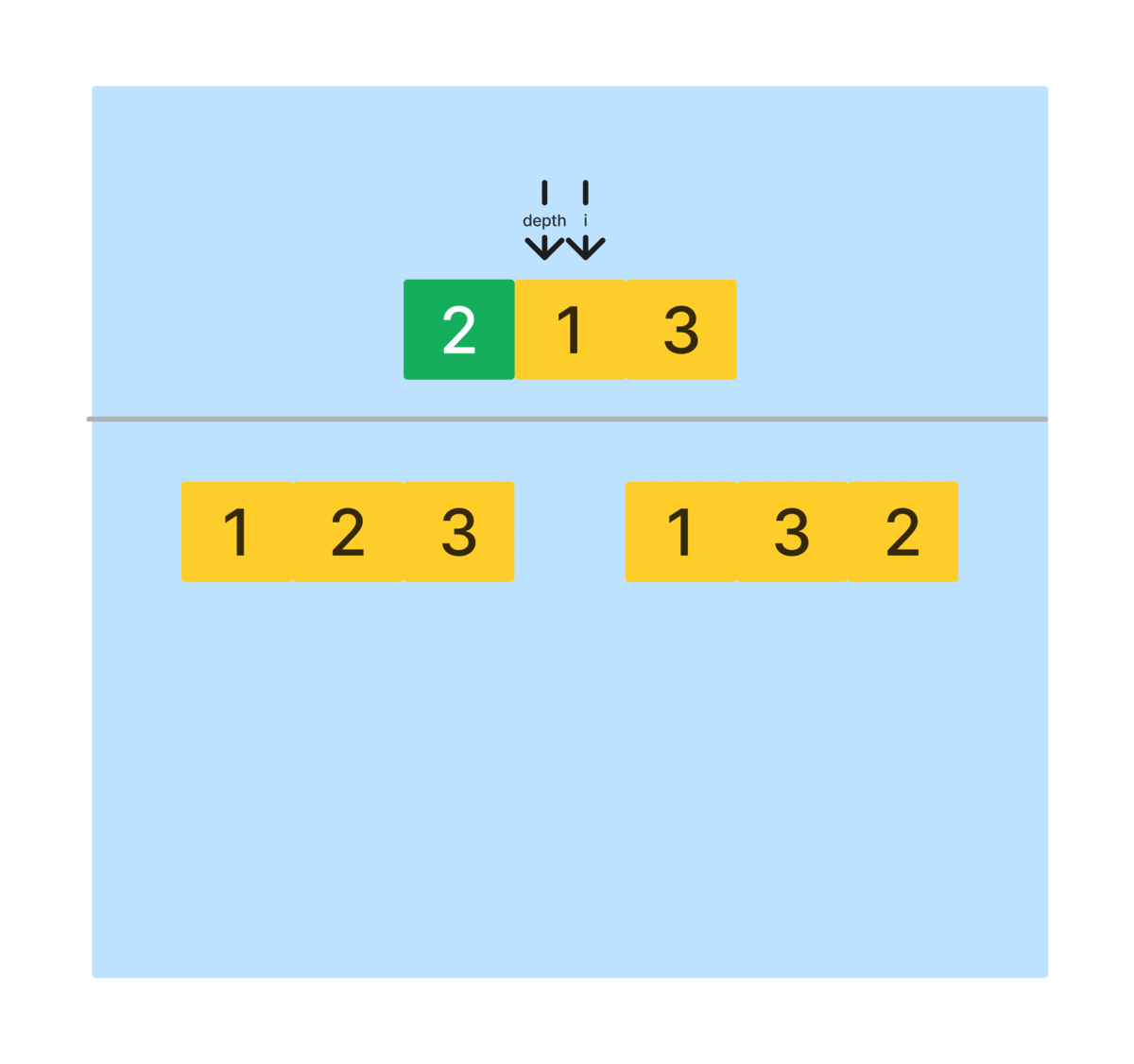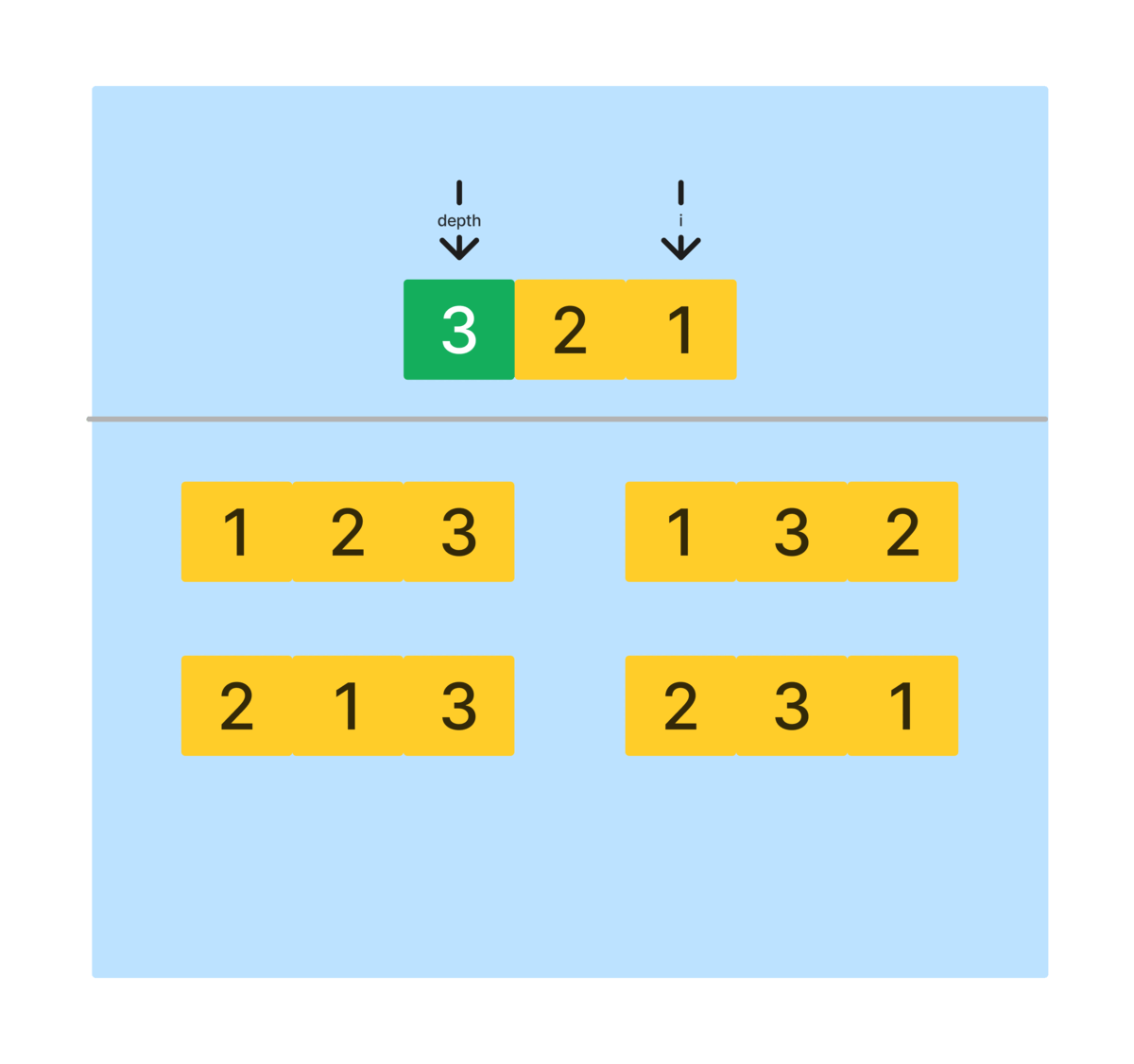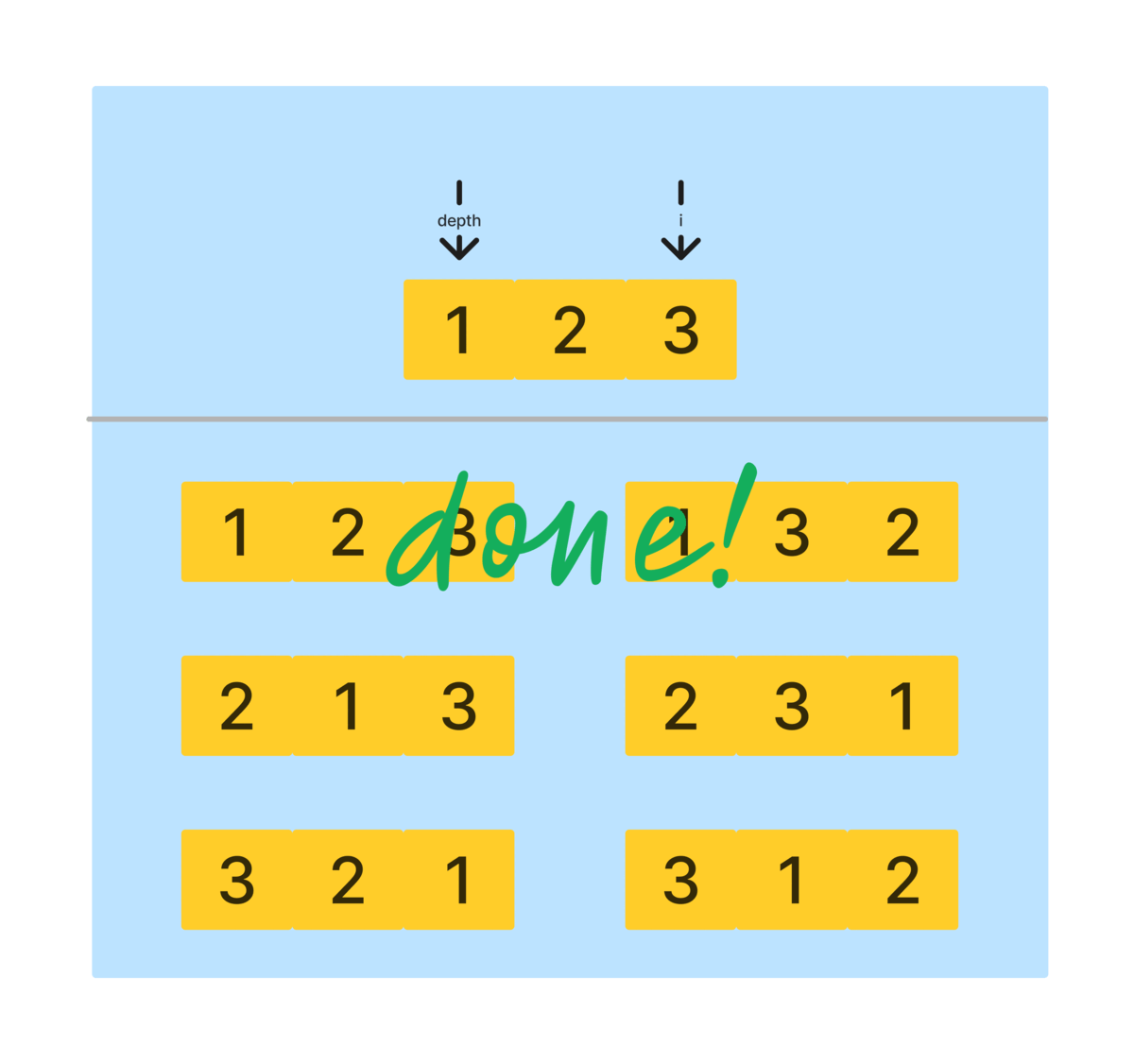
depth가nums.length - 1일 때, 즉, 순열 요소가 만들어졌을 때 종료한다. depth를 시작 인덱스로 반복을 돌면서, 아래와 같은 과정을 반복한다.- depth와 i에 해당하는 배열 요소의 위치를 바꾼다.
- 재귀 호출을 진행한다. 이 때, 다음 요소에 대한 정렬을 진행하기 위해 depth를 한 단계 올린다.
- 재귀 호출이 끝난 경우 swap을 호출해 바뀐 위치를 되돌린다.
- 해당 과정을 모두 종료하게 되면, 모든 요소를 포함하는 순열을 만들 수 있다.
풀이 코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
const swap = (elements: number[], i: number, j: number): void => {
const tmp = elements[i];
elements[i] = elements[j];
elements[j] = tmp;
};
function permute(nums: number[]): number[][] {
const answer: number[][] = [];
const dfs = (arr: number[], depth: number): void => {
if (depth === nums.length - 1) {
answer.push([...arr]);
return;
}
for (let i = depth; i < nums.length; i++) {
swap(arr, depth, i);
dfs(arr, depth + 1);
swap(arr, depth, i);
}
};
dfs([...nums], 0);
return answer;
}
테스트 코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
describe('46. Permutations', () => {
test('example test 1', () => {
const output = permute([1, 2, 3]);
const expected = [
[1, 2, 3],
[1, 3, 2],
[2, 1, 3],
[2, 3, 1],
[3, 1, 2],
[3, 2, 1],
];
expect(output).toEqual(expect.arrayContaining(expected));
});
test('example test 2', () => {
const output = permute([0, 1]);
const expected = [
[0, 1],
[1, 0],
];
expect(output).toEqual(expect.arrayContaining(expected));
});
test('example test 3', () => {
const output = permute([1]);
const expected = [[1]];
expect(output).toEqual(expected);
});
});