234. Palindrome Linked List
문제 설명
단일 연결리스트의 head가 주어질 때, 팰린드롬이면 true 아니면 false를 리턴하라.
해결 방법
런너 기법을 활용하여 절반의 리스트를 뒤집은 뒤, 팰린드롬을 비교한다.
런너 기법은 리스트의 이동하는 두 개 이상의 포인터가 있을 때 이 포인터들의 이동 길이를 다르게 하는 기법이다.
런너 기법을 사용하면 리스트의 1/2, 1/3 등으로 정확히 등분 하기 쉽다.
해당 문제에서는 런너 기법을 활용하여, 리스트의 절반을 뒤집어 팰린드롬을 비교할 것이다.
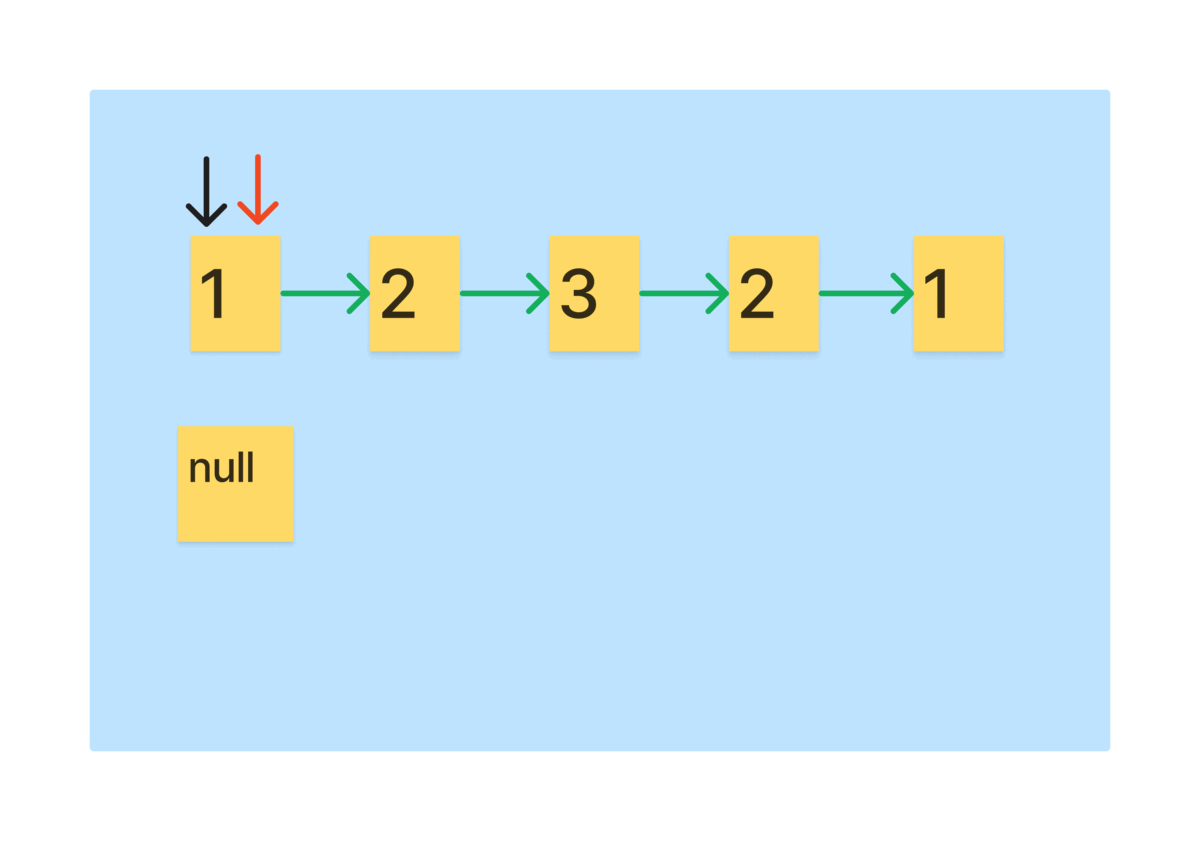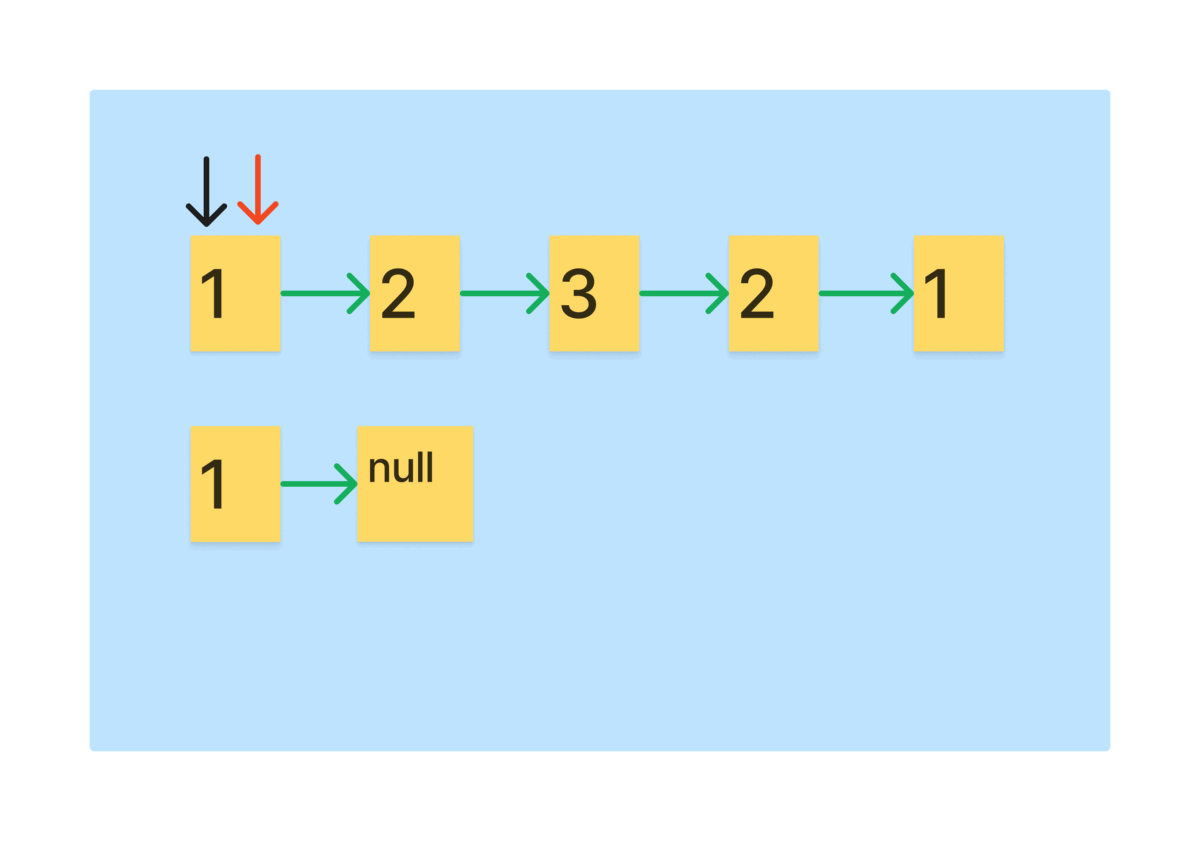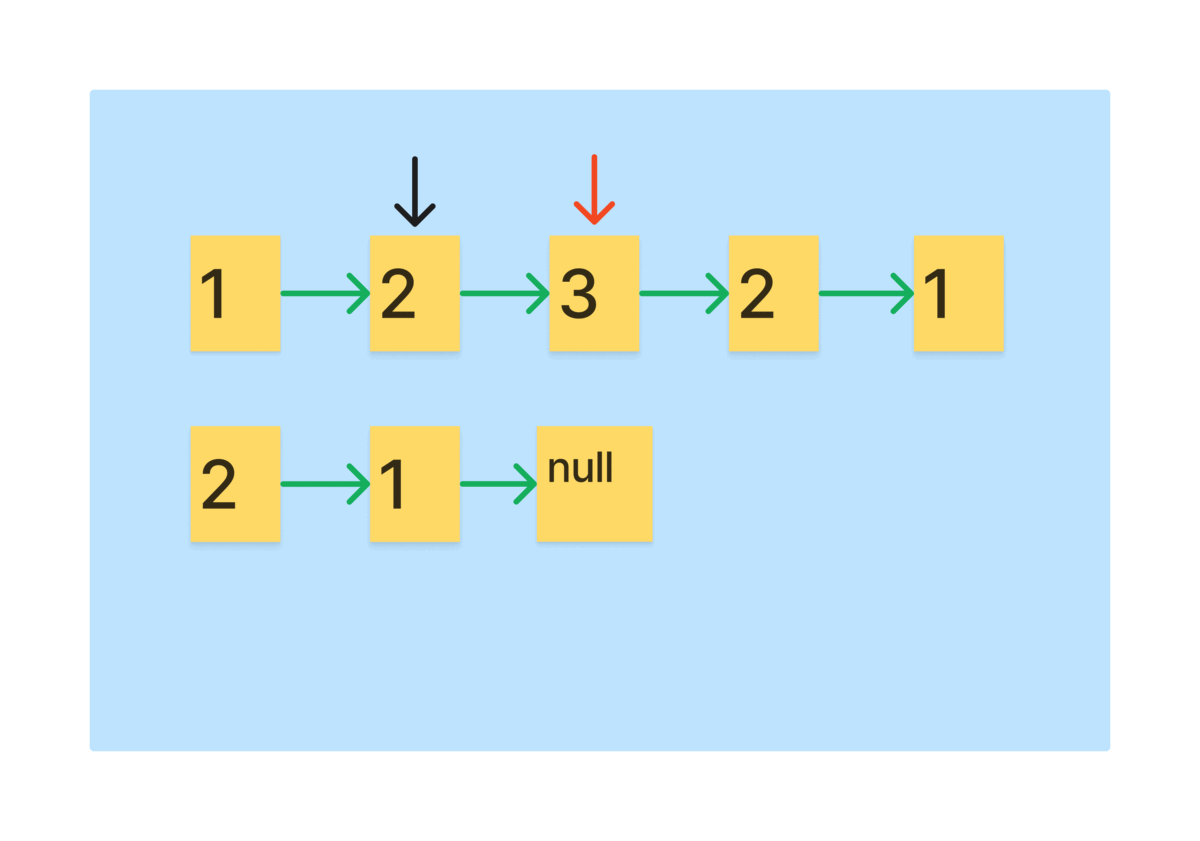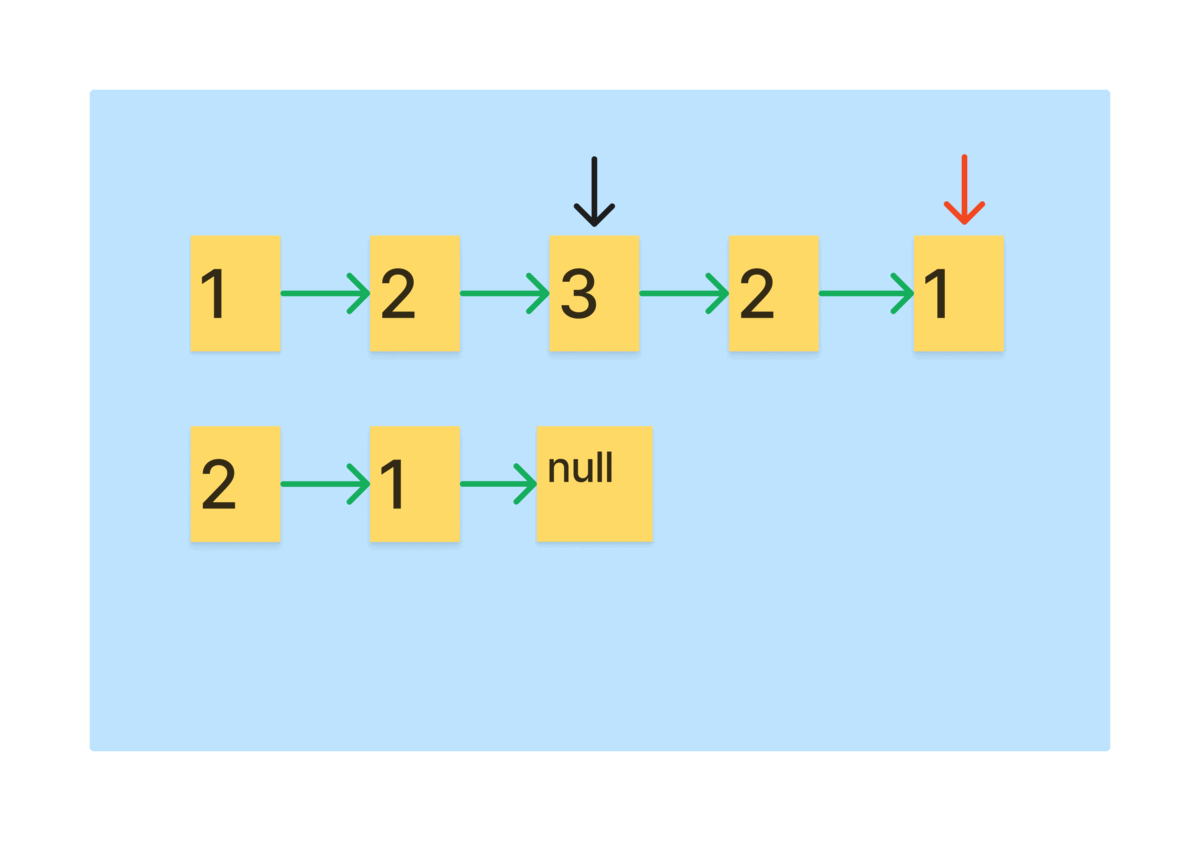
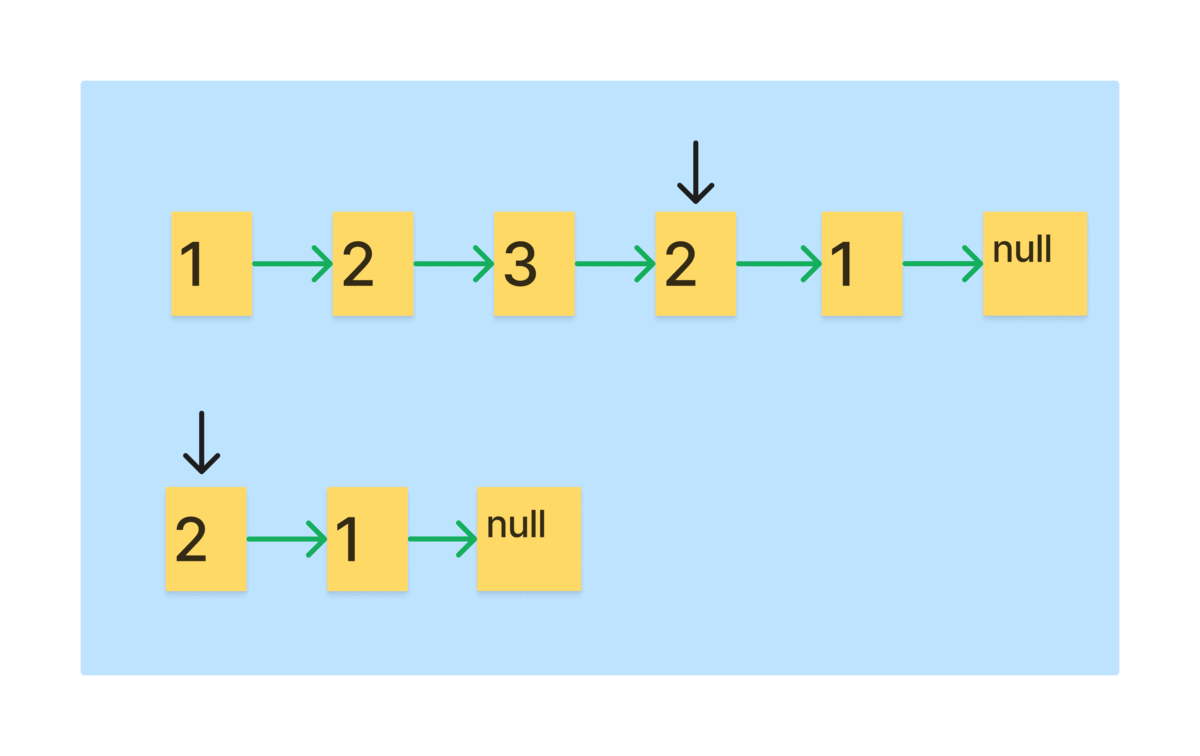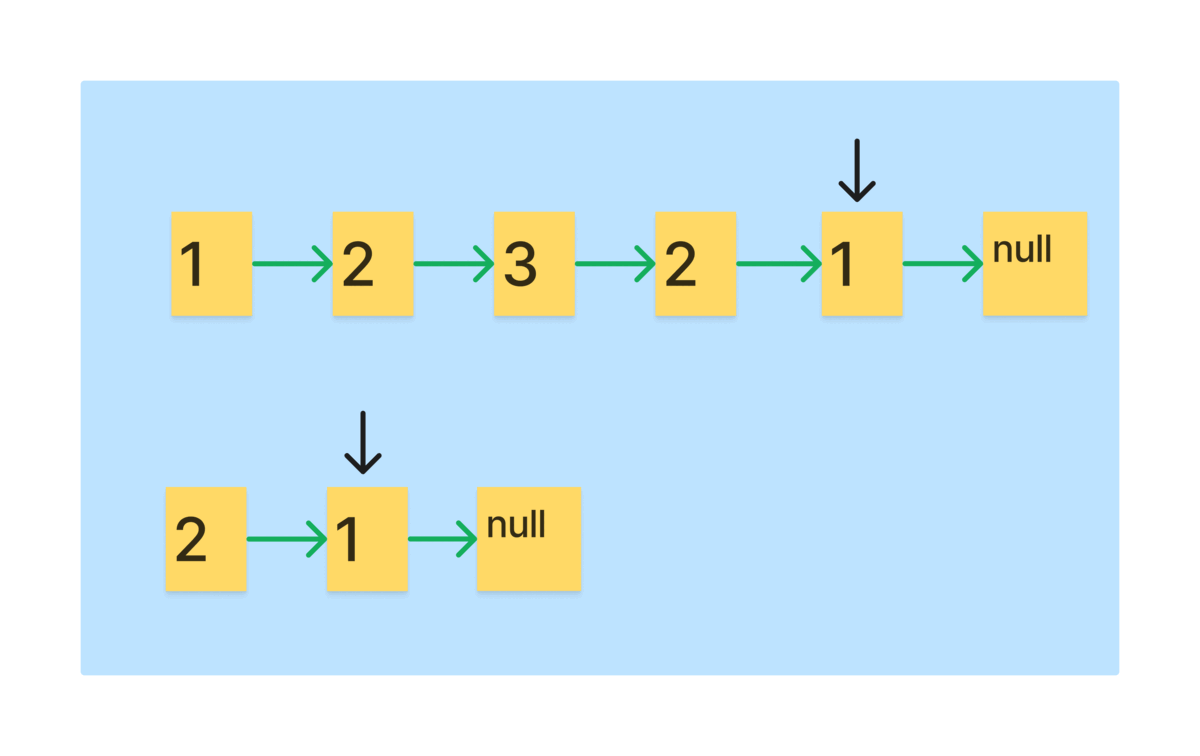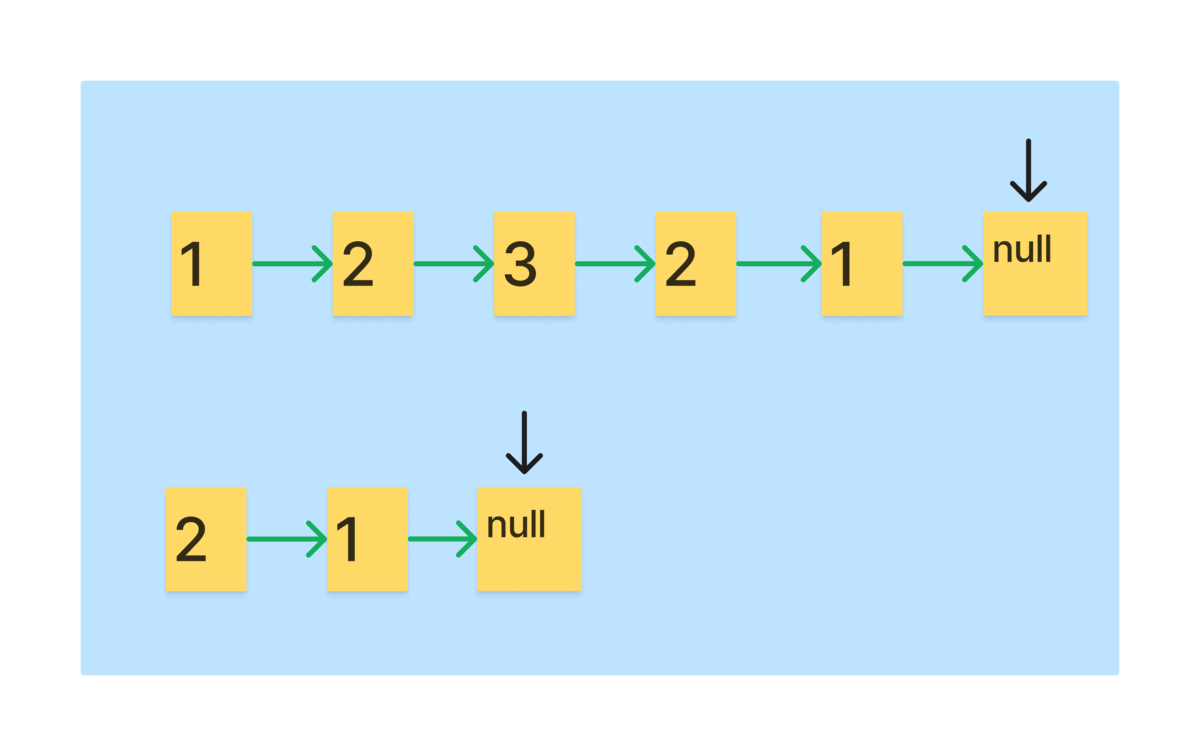
- 리스트를 1칸 이동하는 slow포인터와 2칸 이동하는 fast포인터를 만들고, 역순을 저장하는 리스트를 만든다.
- fast를 끝까지 이동시키면 slow는 정확히 절반을 이동한다.
- 리스트를 순회하면서 slow를 역순 리스트에 head로 만드는 과정을 반복하면 절반의 역순 리스트가 생성된다.
- 역순 리스트와 slow를 비교해 나가면 팰린드롬인지 확인이 가능하다.
먼저, 역순 리스트를 만드는 과정을 그림으로 보자.
이렇게 역순으로 만들었을 때, 리스트의 길이가 홀수여서 slow가 정확히 중앙에 위치하면, 한 칸 이동해야한다.
다음으로 만들어진 역순리스트와 slow를 비교하는 과정을 그림으로 보자.
풀이 코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
// Definition for singly-linked list.
export class ListNode {
val: number;
next: ListNode | null;
constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) {
this.val = val === undefined ? 0 : val;
this.next = next === undefined ? null : next;
}
}
export function isPalindrome(head: ListNode | null): boolean {
let reverseList = null;
let slow = head;
let fast = head;
while (fast && fast.next) {
fast = fast.next.next;
const tmp = reverseList;
reverseList = new ListNode(slow.val, tmp);
slow = slow.next;
}
if (fast) {
slow = slow.next;
}
while (reverseList && reverseList.val === slow.val) {
reverseList = reverseList.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return !reverseList;
}
테스트 코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
import { describe, expect, test } from '@jest/globals';
import { isPalindrome, ListNode } from '.';
describe(' description', () => {
test('example test 1', () => {
const input = new ListNode(
1,
new ListNode(2, new ListNode(2, new ListNode(1)))
);
const output = isPalindrome(input);
const expected = true;
expect(output).toEqual(expected);
});
test('example test 2', () => {
const input = new ListNode(1, new ListNode(2));
const output = isPalindrome(input);
const expected = false;
expect(output).toEqual(expected);
});
});